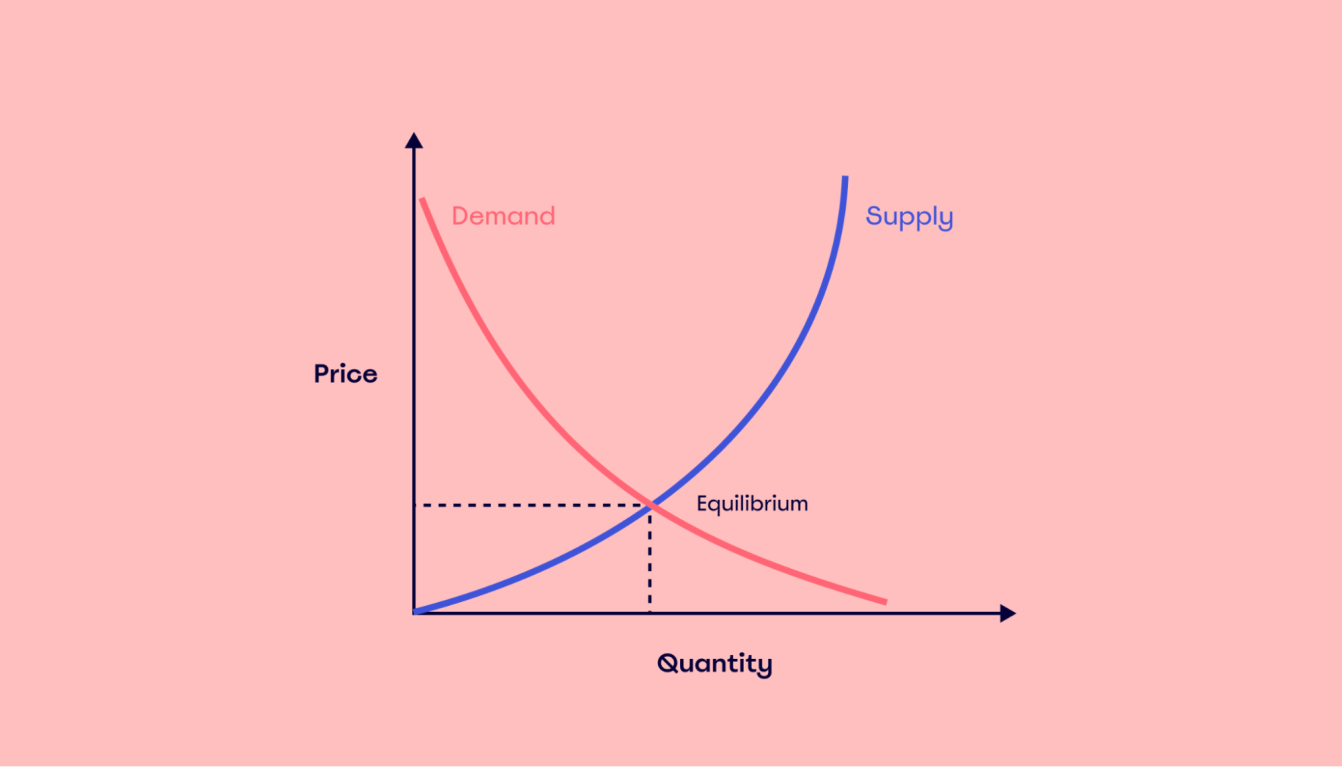
Understanding Supply and Demand
Supply and demand are fundamental concepts in economics that determine the prices of goods and services in a market. Supply refers to the quantity of a product that producers are willing to sell at various prices, while demand represents the quantity that consumers are willing to buy. The interaction between supply and demand sets the equilibrium price, where the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded.
When demand for a product increases, its price tends to rise, encouraging producers to supply more. Conversely, when demand decreases, prices fall, leading to a reduction in supply. This dynamic relationship ensures that markets are efficient and responsive to changes in consumer preferences and production costs. Understanding these principles is crucial for businesses to set competitive prices and for consumers to make informed purchasing decisions.
The concepts of supply and demand also extend to various economic policies and market interventions. For example, governments may impose price controls or subsidies to influence market outcomes. However, such interventions can sometimes lead to unintended consequences, such as shortages or surpluses. Therefore, a thorough understanding of supply and demand is essential for analyzing the potential impacts of economic policies and market dynamics.